Revisiting the Kobe earthquake and the variations of atmospheric radon concentration
Tohoku University researchers have unearthed further details about radon concentration in the atmosphere before and after earthquakes, moving us closer to being able to anticipate when large earthquakes may hit.
The results of their research were published in the journal Science Reports on February 18, 2021.
Radon is a radioactive noble gas derived from radioactive decays of radium-226 in the ground. Radon bubbles up to the surface and is expelled into the atmosphere.
It has long been known that elevated levels of radon underneath the ground can be detected before and after earthquakes. But the relationship between the mechanisms that cause abnormal changes in radon concentration and the occurrence of earthquakes requires greater understanding in order to predict earthquakes accurately.
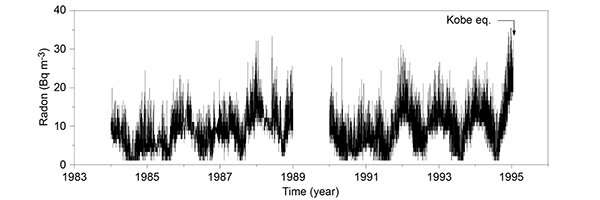
Professor Hiroyuki Nagahama and associate professor Jun Muto of the Graduate School of Science at Tohoku University, in collaboration with Fukushima Medical University and Kobe Pharmaceutical University, analyzed radon concentration data observed before the 1995 Kobe Earthquake.
"We found that there were changes in radon concentration data that originated from tides," said Muto. "This caused periodic loading on the earth's crust."
They also noticed that crustal compression rates on faults near the radon observation point had decreased, and this may have triggered the periodic change in radon concentration.
Radioisotope facilities, which measure the atmospheric radon, exist across Japan.
Muto hopes that their research leads to an increase in radon monitoring across the globe. "We believe that further examination of seismological and geological conditions that differ from Japan will lead to a better understanding of the physical and chemical processes that cause radon concentration variations preceding earthquakes."
More information: Yasutaka Omori et al, Radon degassing triggered by tidal loading before an earthquake, Scientific Reports (2021).
Journal information: Scientific Reports
Provided by Tohoku University