November 12, 2020 report
Researchers make most precise measurements of deuterium fusing with a proton to form helium-3
A large team of researchers affiliated with a host of institutions in Italy, the U.K and Hungary has carried out the most precise measurements yet of deuterium fusing with a proton to form helium-3. In their paper published in the journal Nature, the group describes their effort and how they believe it will contribute to better understanding the events that transpired during the first few minutes after the Big Bang.
Astrophysics theory suggests that the creation of deuterium was one of the first things that happened after the Big Bang. Therefore, it plays an important role in Big Bang nucleosynthesis鈥攖he reactions that happened afterward that led to the production of several of the light elements. Theorists have developed equations that show the likely series of events that occurred, but to date, it has been difficult to prove them correct without physical evidence. In this new effort, the researchers working at the Laboratory for Underground Nuclear Astrophysics in Italy have carried out experiments to simulate those first few minutes, hoping to confirm the theories.
The work was conducted deep under the thick rock cover of the Gran Sasso mountain to prevent interference from cosmic rays鈥攊t involved firing a beam of protons at a deuterium target鈥攄euterium being a form of hydrogen with just one proton and one neutron鈥攁nd then measuring the rate of fusion. But because the rate of fusion is so low, the bombardment had to be carried out many times鈥攖he team carried out their work nearly every weekend for three years.
The hope was that the measured rate would match the amount of cosmic microwave background radiation detected by scientists who have been studying it for many years. Researchers believe such radiation came into existence as the cosmos cooled approximately 380,000 years after the Big Bang.
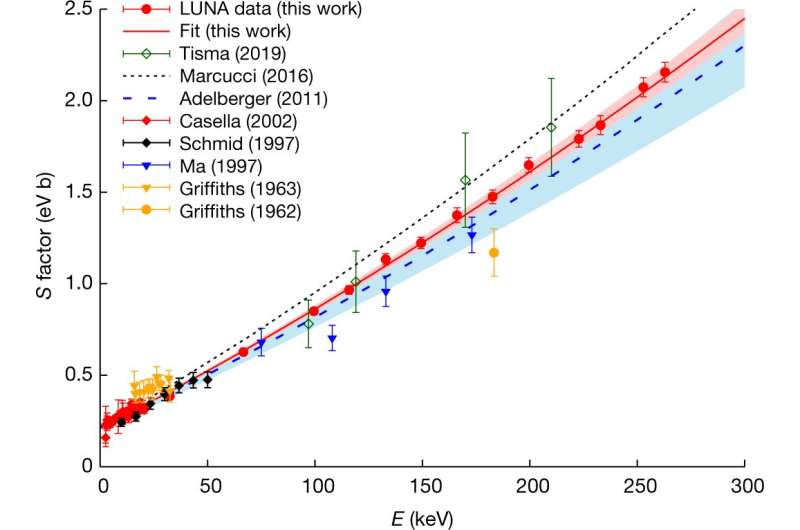
The researchers found that the measured rate of deuterium fusing across a range of temperatures fell between the rate predicted by the latest theories and tentative measurements taken back in 1997, the last time scientists tried to measure the rate of deuterium fusing with a proton to form helium-3. But most importantly, when they plugged the rate they measured into models that projected Big Bang nucleosynthesis density estimates, it closely matched estimated measurements of the CMB 380,000 years later.
More information: V. Mossa et al. The baryon density of the Universe from an improved rate of deuterium burning, Nature (2020).
Journal information: Nature
漏 2020 Science X Network